Iran's Healthcare System: A Blend Of Progress & Challenges
Exploring the intricate dynamics of the **health care system in Iran** reveals a fascinating journey of reform, resilience, and ambition. For decades, Iran has strived to build a robust healthcare infrastructure, navigating a complex landscape of societal needs, economic pressures, and global influences. This comprehensive overview delves into the structure, achievements, and ongoing challenges that define healthcare delivery in the Islamic Republic of Iran, offering valuable insights into its unique approach to public well-being.
From its constitutional commitment to universal access to its innovative primary healthcare programs, the Iranian healthcare system stands as a testament to the nation's dedication to its citizens' health. While facing significant hurdles, particularly concerning external impacts on resource availability, Iran continues to evolve its health policies and services, aiming to ensure quality and accessible care for all.
Table of Contents
- The Foundation of Iran's Healthcare System
- Structure and Funding: Public vs. Private
- Notable Achievements and Global Recognition
- Key Reforms and Ongoing Transformations
- Challenges Facing Iran's Healthcare System
- Cultural Influences and Future Prospects
- Biotechnology and Medical Research
- Navigating Iran's Healthcare: A Comprehensive Overview
The Foundation of Iran's Healthcare System
The development of the **health care system in Iran** is deeply rooted in its post-revolution constitutional principles and a long-standing commitment to public welfare. The journey has been marked by significant structural and organizational reforms, reflecting the nation's evolving understanding of health equity and access.
Constitutional Mandate and Early Reforms
Following the 1979 revolution, the Constitution of the Islamic Republic of Iran enshrined a constitutional mandate in Article 29 to provide universal access to basic health services. This foundational commitment laid the groundwork for a predominantly public healthcare system, with the government assuming a crucial role in service provision. A pivotal moment in this development was the establishment of the national health network in 1983. This ambitious reform aimed to drastically reduce inequities and expand healthcare coverage and access, particularly in deprived and rural areas. The Iranian government has since implemented several other reforms, including the introduction of the family physician program, further solidifying its commitment to widespread access.
The Pivotal Role of Primary Health Care
One of the most important and successful components of Iran's healthcare system is its robust primary health care (PHC) program. Dating back to efforts made during the 1980s, Iran has long been recognized for its success in PHC, largely due to an innovative approach centered around community health workers. The international community's decision on the adoption of primary health care was a significant historical event in the development and delivery of health services, aiming to achieve community justice in access to basic health services. Iran embraced this philosophy early on, implementing its PHC program in the 1980s. This community-centric model has been instrumental in extending basic health services to remote areas, significantly improving public health outcomes and contributing to rural poverty alleviation. The emphasis on prevention, health promotion, and accessible first-line care remains a cornerstone of the Iranian health system's strategy.
Structure and Funding: Public vs. Private
The **health care system in Iran** operates as a blend of public and private healthcare services, though it is predominantly public. The government plays a crucial role in providing the majority of healthcare services, with state-run hospitals, clinics, and health centers forming the backbone of the system. According to the Ministry of Health and Medical Education (MOHME), the government provides approximately 80% of the country's healthcare services. This public dominance is largely due to the constitutional mandate for universal access and the government's commitment to ensuring basic healthcare for all citizens.
The private sector, while present, is involved mainly in specialized services, private clinics, and a limited number of private hospitals. While it offers an alternative for those who can afford it, the cost of private healthcare services remains a significant barrier for a large segment of the population. Data from MOHME indicates that 80% of the country's population cannot afford the tariffs charged by the private sector for healthcare services. This highlights a persistent challenge in ensuring equitable access across different socioeconomic strata, even within a system that prioritizes public provision. Funding for the public sector primarily comes from government budgets, public health insurance schemes, and out-of-pocket payments, though efforts are continuously made to reduce the latter through various reforms.
Notable Achievements and Global Recognition
Despite the challenges, the **health care system in Iran** has achieved remarkable successes and garnered international recognition for its efficiency and progress. These achievements underscore the nation's commitment to improving public health indicators and expanding access to quality care.
A significant highlight came in 2016 when Bloomberg News ranked Iran as the 30th most efficient healthcare system globally, notably placing it ahead of developed nations like the United States and Brazil. This ranking was a testament to Iran's ability to deliver health outcomes effectively relative to its spending. The report further showed impressive figures for life expectancy in Iran, reaching 75.5 years, a substantial improvement over past decades. Per capita spending on healthcare was reported at $346, indicating a relatively efficient use of resources to achieve these health outcomes.
Beyond these statistics, Iran's motivation to improve its healthcare infrastructure in recent decades has resulted in surprising figures, particularly in rural areas. The expansion of primary health care services and the establishment of health houses (Khaneh Behdasht) have significantly contributed to rural poverty alleviation by reducing health-related financial burdens and improving overall community well-being. These efforts have not only extended the reach of healthcare but also empowered local communities through innovative approaches centered around community health workers. The continuous transformation of the health system of the Islamic Republic of Iran, coupled with its historical success in primary health care, paints a picture of a nation making substantial strides in public health.
Key Reforms and Ongoing Transformations
The **health care system in Iran** has been in a state of continuous transformation, undergoing several structural and organizational reforms over the past three decades. These reforms reflect a dynamic approach to addressing evolving health needs and improving the efficiency and equity of healthcare delivery.
One of the most significant reforms, as previously mentioned, was the establishment of the national health network in 1983, which aimed to reduce inequities and expand coverage and access to health care in deprived areas. Building on this foundation, the Iranian government has implemented several other crucial reforms. In 1980, the primary health care system was established, followed by the integration of medical education with health care services in 1985. This integration was a strategic move to ensure that medical training was directly aligned with the practical needs of the healthcare system, fostering a more holistic approach to health service delivery.
Further strengthening the system, the establishment of the public health insurance law in 1994 marked a significant step towards financial protection for households and universal health coverage. More recently, the Health Transformation Plan (HTP), notified to medical universities on May 5, 2014, represents the latest comprehensive reform of Iran's health system. The HTP's core objectives are multifaceted: to facilitate access to universal health coverage, provide financial protection for households against catastrophic health expenditures, ensure justice in access to health services for all society members, and enhance the overall efficiency of the health system. This plan has been instrumental in modernizing various aspects of healthcare, including the hospital system, aiming for a more streamlined and patient-centered approach. These ongoing transformations underscore Iran's proactive stance in adapting its healthcare policies to meet contemporary challenges and achieve its long-term health goals.
Challenges Facing Iran's Healthcare System
Despite its notable achievements and continuous reforms, the **health care system in Iran** faces a unique set of challenges, many of which are influenced by external factors and internal complexities. These hurdles impact the system's performance, affordability, and public satisfaction.
One of the most significant challenges stems from the indirect negative impact of external events, which have resulted in increased healthcare costs and reduced availability and affordability of medicines and medical equipment. These pressures can strain the supply chain for essential medical supplies, making it difficult for both public and private sectors to maintain consistent service quality. Consequently, the performance of Iranian hospitals has, at times, decreased, leading to a drop in public satisfaction with the healthcare system. Ensuring a stable and affordable supply of medical necessities remains a critical concern for policymakers.
Furthermore, while the system has made strides, there are complexities in fully alleviating the burden of diseases. For instance, some reports indicate that the alleviation of the burden of diseases in Iran following the 2004 and 2014 periods was not fully captured, suggesting potential gaps in data collection or persistent challenges in controlling certain health conditions. This highlights the ongoing need for robust epidemiological surveillance and targeted interventions. The predominantly public nature of the system, while beneficial for access, also means it is highly susceptible to government budget fluctuations and economic downturns. Balancing the constitutional mandate for universal access with the realities of funding and resource constraints is a perpetual balancing act for the Iranian healthcare authorities. Addressing these multifaceted challenges requires continuous adaptation, strategic resource allocation, and a commitment to innovation.
Cultural Influences and Future Prospects
The **health care system in Iran** is not merely a collection of institutions and policies; it is also deeply influenced by cultural norms, societal values, and the unique historical trajectory of the nation. These influences shape how healthcare services are delivered, perceived, and utilized by the population.
The emphasis on community health workers and the family physician program, for instance, reflects a cultural preference for personalized, localized care that integrates into the fabric of daily life. The strong public sector presence is also a manifestation of the constitutional mandate for "health for all," a principle that resonates deeply within Iranian society. Various initiatives within the system aim to ensure access to quality health services for all citizens, reflecting a broader societal commitment to health equity. This includes ongoing efforts to modernize facilities, train healthcare professionals, and expand health insurance coverage to reach underserved populations.
Looking to the future, the health system of the Islamic Republic of Iran is clearly under transformation. This ongoing evolution suggests a dynamic and adaptive approach to healthcare delivery. Future prospects involve continued investment in primary care, further integration of technology, and a focus on preventative health measures to address emerging health challenges. The lessons learned from past reforms, both successes and challenges, will undoubtedly inform future policy decisions. The aim is to build a more resilient, equitable, and efficient healthcare system that can effectively meet the health needs of a growing and diverse population, while also adapting to global health trends and internal socioeconomic shifts. The debate surrounding the characteristics, progresses, and challenges of the Iranian health system will continue to shape its trajectory, pushing it towards greater effectiveness and public satisfaction.
Biotechnology and Medical Research
An often-overlooked yet critical aspect of the **health care system in Iran** is its growing emphasis on scientific research and technological advancement, particularly in the fields of biotechnology and microbiology. Iran recognizes that innovation in these areas is crucial for developing advanced diagnostic tools, effective treatments, and new pharmaceutical products, ultimately enhancing the quality and efficacy of healthcare services.
The National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) provides access to biomedical and genomic information, supporting research and discovery in health, science, and medicine globally. While not exclusively Iranian, Iran's scientific community actively engages with and contributes to such global repositories of knowledge. Iranian researchers and institutions are increasingly involved in exploring insights into biotechnology and microbiology research, leveraging comprehensive resources and scientific articles to advance their work. This commitment to research is evident in the establishment of various research centers and the integration of medical education with healthcare services, which fosters a culture of inquiry and innovation among medical professionals.
Investment in biotechnology is seen as a strategic imperative for Iran, not only to improve domestic healthcare capabilities but also to reduce reliance on foreign imports for essential medicines and medical technologies. By fostering a vibrant research environment, the Iranian healthcare system aims to develop localized solutions for prevalent diseases, contribute to global scientific advancements, and ensure that its healthcare services are at the forefront of medical innovation. This focus on scientific progress is a testament to Iran's long-term vision for a self-reliant and advanced healthcare sector.
Navigating Iran's Healthcare: A Comprehensive Overview
In conclusion, the **health care system in Iran** presents a compelling case study of a nation's enduring commitment to public health. From its constitutional mandate for universal access following the 1979 revolution to its globally recognized primary healthcare programs, Iran has built a predominantly public system designed to serve all its citizens. The journey has been marked by significant reforms, including the establishment of the national health network in 1983, the integration of medical education with health services, and the ambitious Health Transformation Plan of 2014, all aimed at achieving universal health coverage, financial protection, and justice in access.
While celebrated for achievements such as its Bloomberg ranking for efficiency, improved life expectancy, and success in rural poverty alleviation, the system is not without its challenges. External pressures leading to increased costs and reduced availability of medicines, along with complexities in measuring the full alleviation of disease burdens, continue to test its resilience. Yet, Iran's ongoing transformation, its strategic investment in biotechnology and medical research, and its unique blend of public and private services underscore a proactive approach to healthcare delivery.
Understanding the Iranian healthcare system offers valuable insights into how a nation can strive for health equity amidst complex circumstances. We hope this article has provided a comprehensive overview, detailing its public and private sectors, funding sources, regulatory framework, and the challenges it faces. What are your thoughts on the balance between public and private healthcare provision? Share your perspectives in the comments below, or explore other articles on our site to deepen your understanding of global health systems.
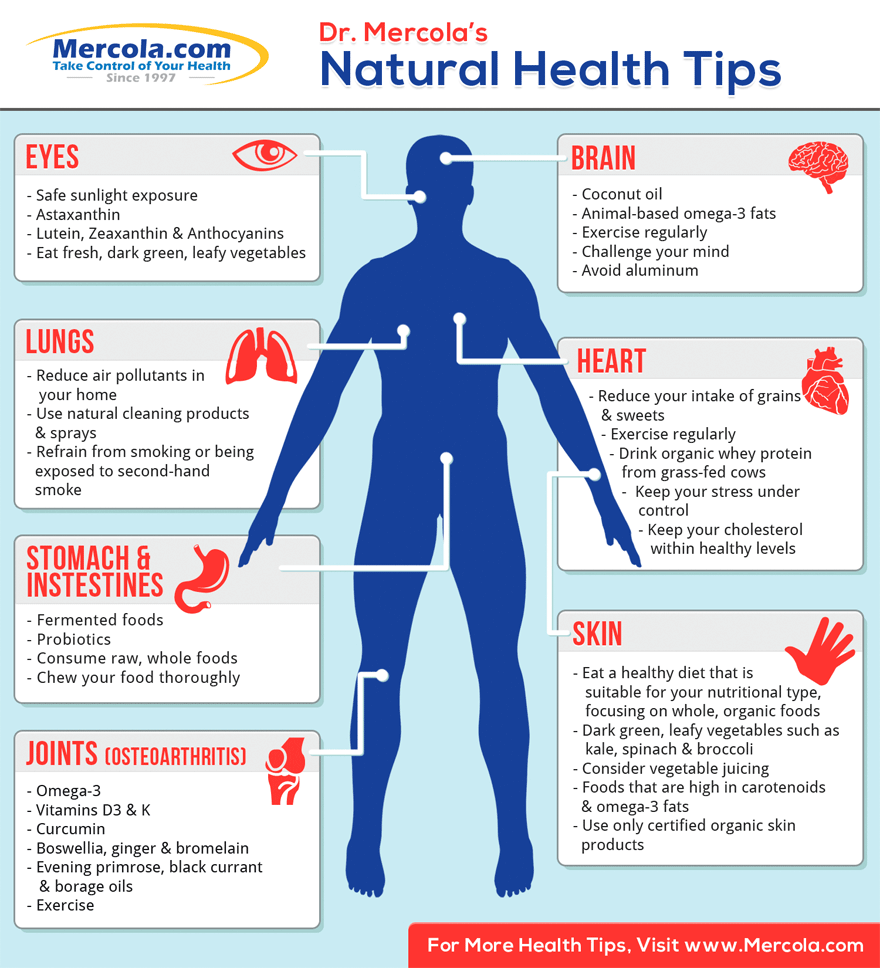
10 Health and Fitness Infographics That You Need To See
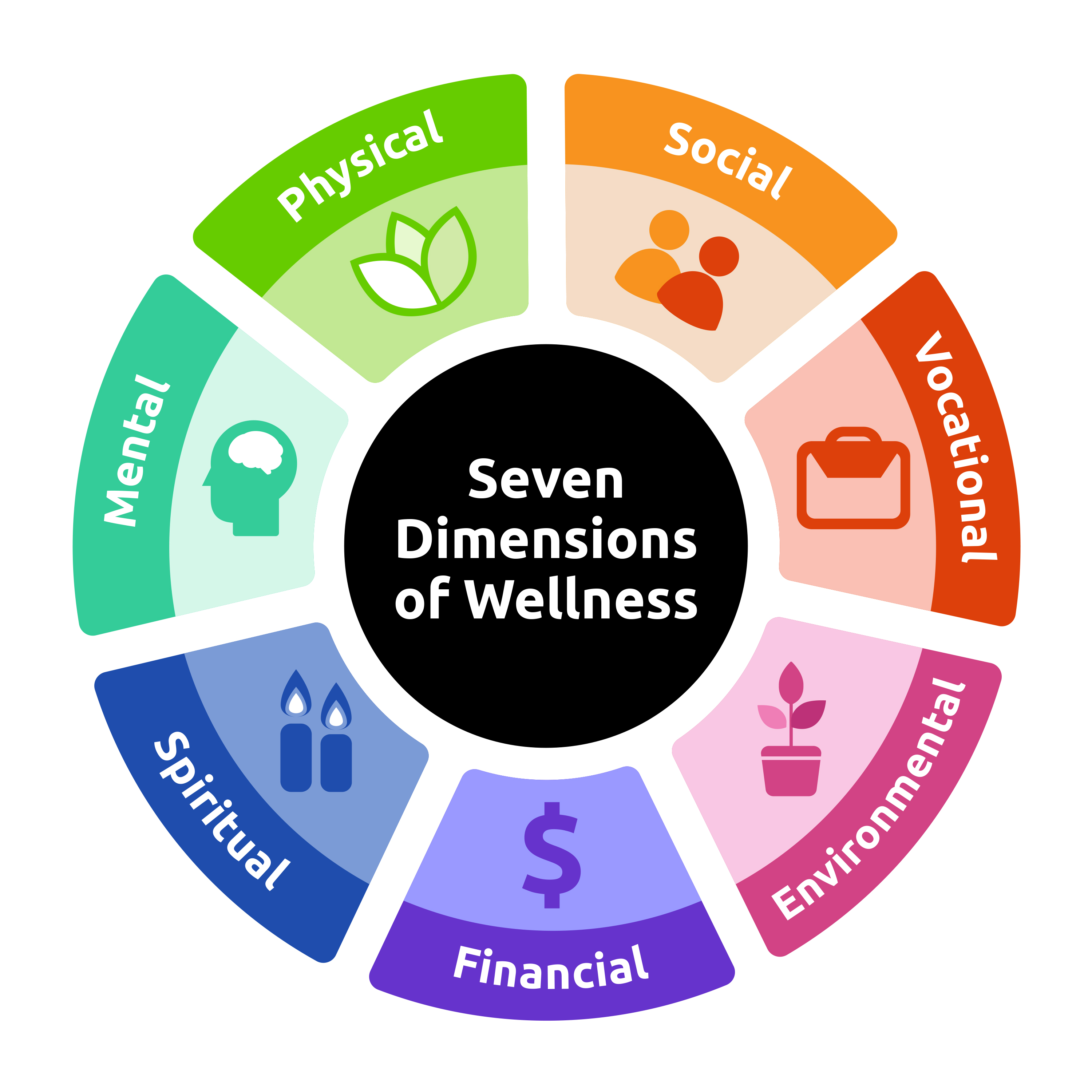
Health And Wellness 2023 - Image to u

All About Health | Rockford Regional Health Council