Navigating Health Insurance In Iran: A Comprehensive Guide
Table of Contents
- The Pillars of Iranian Healthcare and Its Economic Footprint
- Evolution of Iranian Health Insurance: A Journey to UHC
- Public Health Insurance in Iran: The Foundation of Coverage
- Private Health Insurance Options and Their Role
- Health Insurance for Expats and Refugees in Iran
- Stewardship, Financing, and Challenges in the Health Insurance Ecosystem
- The Iran Health Insurance Fund and Systemic Integration
- Digitalization and the Future of Health Insurance in Iran
The Pillars of Iranian Healthcare and Its Economic Footprint
Iran's healthcare system is a complex yet effective structure, built upon three fundamental pillars. This comprehensive overview of Iran's healthcare system details its public and private sectors, funding sources, and regulatory framework. The country has long been recognized for its success in primary healthcare, an achievement dating back to efforts made during the 1980s, largely due to an innovative approach centered around community health workers. This foundational strength has paved the way for a health system that, despite undergoing transformation, remains committed to ensuring access to quality health services for all citizens. The economic significance of the healthcare and medical sector in Iran is substantial and growing. In 2002, the market value of this sector was estimated at nearly US$24 billion. Projections indicated a significant rise, with forecasts suggesting it could reach US$96 billion. This growth underscores the increasing investment and importance placed on healthcare services within the national economy, further highlighting the crucial role of **health insurance in Iran** as a financial enabler for both providers and patients. The Ministry of Health and Medical Education, alongside various health insurance schemes, plays a pivotal role in devising and following policies aimed at controlling healthcare expenditures, especially in the pursuit of Universal Health Coverage (UHC).Evolution of Iranian Health Insurance: A Journey to UHC
The journey towards comprehensive health coverage in Iran has been a long and deliberate one, marked by significant reforms and strategic initiatives. The synthesized evidence and findings regarding the evolution of the Iranian health insurance system indicate that its development can be categorized into six major periods, each defined by key steps undertaken to reach Universal Health Coverage (UHC). This historical progression reflects a continuous effort to expand access and improve the quality of healthcare services for the entire population. Social health insurance, both globally and specifically in Iran, has been a central focus for policymakers and researchers like Takian A., Rashidian A., and Doshmangir L., who have proposed various models for its implementation. These efforts are part of a broader national strategy to ensure that financial barriers do not prevent individuals from accessing necessary medical care. The ultimate goal of UHC in Iran necessitates a robust and adaptable health insurance framework that can evolve with the country's demographic and economic changes.Legislative Milestones and the UHI Law
The legislative landscape surrounding **health insurance in Iran** is extensive and dynamic. Records show that there have been 245 recognized laws pertaining to health insurance in Iran enacted between 1971 and the end of 2021. A significant turning point in this legislative history was the Universal Health Insurance (UHI) Law. Of these numerous laws, only 20 were passed before the UHI Law, while a staggering 225 laws have been enacted afterward. This proliferation of legislation post-UHI Law underscores the profound impact and ongoing efforts to refine and expand health insurance coverage across the nation. The UHI Law in 2021 marked a pivotal moment, aiming to investigate the network of actors within the health insurance ecosystem both before and after its implementation. This law signifies a concentrated push towards greater inclusivity and efficiency within the system, shaping how various entities—from the Ministry of Health to individual insurance providers—interact and contribute to the overall health of the populace.Public Health Insurance in Iran: The Foundation of Coverage
The cornerstone of **health insurance in Iran** for its citizens and long-term residents is the public health insurance system. Under this system, Iranian citizens and residents are automatically covered, providing them with access to basic healthcare services primarily at public hospitals. This foundational coverage is designed to ensure that a broad spectrum of the population has at least a basic level of financial protection against medical expenses. The public system operates on principles of social equity, aiming to reduce out-of-pocket expenses for essential medical and diagnostic services. It covers some or all of the cost of medical expenses, including doctor visits, hospital stays, and prescription medications, within its defined scope. For those in need, there are ongoing efforts to implement working mechanisms that extend free health insurance coverage, further solidifying the commitment to universal access and support for vulnerable populations. This commitment aligns with the broader objective of achieving UHC, where financial protection is extended to all segments of society.Private Health Insurance Options and Their Role
While the public system provides fundamental coverage, the Iranian health insurance landscape also features a significant private sector. This segment offers a wide array of products, ranging from life and motor insurance to health and property coverage, tailored to meet the needs of individuals, families, and businesses seeking more comprehensive or specialized services. The country’s insurance industry has grown significantly over the years, becoming a vital part of Iran's economy, reflecting a maturing market with diverse offerings. Private health insurance in Iran serves as a crucial complement to the public system. It is often sought by individuals who desire: * **Access to Private Facilities:** Coverage for private hospitals and clinics, which may offer shorter wait times, more specialized services, or different amenities. * **Enhanced Coverage:** Broader coverage for services not fully covered by the public system, such as certain diagnostic tests, specialized treatments, or elective procedures. * **Greater Choice:** The ability to choose specific doctors or specialists outside the public network. * **Financial Security:** Additional financial protection against unforeseen and potentially high costs of private medical care, which can quickly add up, especially given the general excellence of healthcare in the country. For many, particularly those with higher incomes or specific health needs, combining public coverage with private health insurance provides a robust safety net, ensuring access to both general healthcare and more specialized treatments.Health Insurance for Expats and Refugees in Iran
The question of **health insurance in Iran** takes on a unique dimension for non-citizens, including expatriates and refugees. Their access to healthcare services and the mechanisms for financial coverage differ significantly from those for Iranian citizens.Expats: Securing Your Health Coverage
For expatriates, securing appropriate medical coverage is not just recommended but often essential. There are few, if any, reciprocal medical arrangements between Iran and other countries. This means that expats will therefore need private medical insurance, regardless of whether they plan to use public or private healthcare services. This is a critical point, as relying solely on the public system without proper private coverage can lead to significant out-of-pocket expenses. International health insurance is strongly recommended for Iran, regardless of whether insurance is mandatory for your specific visa application. While the healthcare in the country is generally excellent, the costs of private care can quickly add up, especially given any security risks that might necessitate specialized or emergency medical attention. Fortunately, for many expats, their employers will typically cover this expense in Iran, making it a standard benefit for foreign workers. This employer-sponsored coverage often includes comprehensive plans that cater to the specific needs of international residents, ensuring access to a wide range of services and facilities.Refugee Healthcare Coverage
In a commendable display of humanitarian commitment, Iran extends significant healthcare provisions to refugees within its borders. All diagnostic and treatment services for refugees are covered in all hospitals contracted with the Iran Health Insurance Organization (IHIO) countrywide, similar to Iranians. This policy ensures that one of the most vulnerable populations has access to essential medical care, alleviating a major burden for those who have sought refuge in the country. This inclusive approach highlights Iran's dedication to public health and universal access, even for non-citizens in dire need.Stewardship, Financing, and Challenges in the Health Insurance Ecosystem
The effective functioning of Iran’s health insurance system, viewed as an ecosystem, hinges on identifying and exploiting stewardship and financing challenges. This is essential for achieving predetermined goals, particularly the overarching objective of UHC. A recent study aimed to determine the challenges and strategies within the Iranian health insurance ecosystem to provide relevant evidence to healthcare managers and policymakers to improve its functions and perform necessary reforms. Key challenges often revolve around: * **Cost Control:** Managing healthcare expenditures remains a significant hurdle. To achieve UHC, the Ministry of Health and Medical Education and health insurance schemes must devise and follow policies to control healthcare expenditures. * **Equity in Access:** While efforts are made to extend free health insurance coverage for those in need, ensuring truly equitable access across all regions and socioeconomic groups remains an ongoing challenge. * **Regulatory Framework:** Despite 245 recognized laws in health insurance from 1971 to 2021, constant analysis and updating of the regulatory framework are needed to keep pace with evolving healthcare needs and economic realities. * **Data and Research Gaps:** More studies are needed to fully understand the complexities of the system and inform evidence-based policymaking. Insights from interviews with health insurance stakeholders, summarized in various reports, provide valuable qualitative data for this purpose.Addressing Challenges and Future Prospects
The health system of the Islamic Republic of Iran is under continuous transformation. This ongoing evolution is driven by a desire to overcome existing challenges and enhance the efficiency and reach of **health insurance in Iran**. Future prospects include: * **Strengthening Primary Healthcare:** Building on its historical success in primary healthcare, Iran aims to further integrate and strengthen this foundational level of care, which can significantly reduce the burden on more expensive specialized services. * **Digitalization:** The embrace of electronic systems (سامانه های الکترونیکی) by major players like Bimeh Iran (Iran Insurance) signifies a move towards greater efficiency, transparency, and accessibility. Platforms like Samaneh Darman Electronic (SADA) for electronic treatment, online premium payment systems, and mobile applications are transforming how citizens interact with their insurance providers. * **Strategic Mergers:** The idea of merging healthcare insurance funds into the Iran Health Insurance Fund, along with calculating the real costs of medical and diagnostic services, tariffs, and cost leadership/governance, is a strategic move to streamline operations and improve financial management. * **Human Capital Development:** Analyzing and updating training programs for courses meeting the health system needs, and planning and implementing ongoing education for employees at a managerial level, are crucial for building a skilled workforce capable of navigating and leading the complex health insurance ecosystem. These initiatives collectively aim to refine the system, ensuring its sustainability and effectiveness in providing financial protection and access to quality healthcare for all.The Iran Health Insurance Fund and Systemic Integration
At the heart of Iran's public health insurance system is the Iran Health Insurance Fund (IHIF), a pivotal entity responsible for managing and distributing health insurance resources. The concept of merging various healthcare insurance funds into the IHIF is a strategic move aimed at consolidating resources, improving efficiency, and standardizing practices across the board. This integration facilitates a more cohesive approach to healthcare financing and delivery. A key aspect of the IHIF's mandate involves calculating the real costs of medical and diagnostic services, tariffs, and implementing robust cost leadership/governance. This meticulous approach to cost analysis is crucial for ensuring the financial viability of the system and for setting fair and transparent tariffs for services. By accurately assessing costs, the IHIF can better allocate resources, prevent financial leakages, and ensure that the funds are utilized effectively to benefit insured individuals. This centralized management under the IHIF also plays a significant role in analyzing and updating training programs for courses meeting the health system needs, as well as planning and implementing ongoing education for employees at a managerial level, thereby strengthening the human capital within the health insurance sector. This systemic integration is vital for the long-term sustainability and effectiveness of **health insurance in Iran**.Digitalization and the Future of Health Insurance in Iran
The future of **health insurance in Iran** is increasingly intertwined with digitalization. Leading insurance companies like Bimeh Iran (Iran Insurance) are at the forefront of this transformation, embracing electronic systems (سامانه های الکترونیکی) to enhance service delivery and customer experience. These digital platforms are revolutionizing how individuals access and manage their health insurance. Key digital initiatives include: * **Samaneh Darman Electronic (SADA):** An electronic treatment system that streamlines processes related to medical services, from appointments to claims. * **Online Payment Systems:** Convenient internet payment options for installments and premiums, making it easier for policyholders to manage their financial obligations. * **Online Agency Applications:** Systems for registering and tracking requests for life insurance agencies, indicating a broader digital transformation across various insurance products. * **Mobile Applications:** Companion apps that provide on-the-go access to insurance information, policy details, and service requests, bringing insurance services directly to the users' fingertips. These advancements signify a commitment to leveraging technology to make **health insurance in Iran** more accessible, transparent, and efficient for all citizens and residents. As the country continues its journey towards UHC, digitalization will undoubtedly play an even more critical role in bridging gaps, improving service quality, and ensuring that financial protection against medical costs is readily available to everyone.Conclusion
**Health insurance in Iran** is a dynamic and evolving system, fundamental to the country's commitment to universal healthcare access. From its historical roots and legislative milestones, particularly the impactful UHI Law, to its current dual public and private landscape, the system is designed to provide crucial financial protection against medical expenses. While Iranian citizens and residents benefit from automatic public coverage, expatriates and refugees also have specific provisions, with private international insurance strongly recommended for the former, and comprehensive coverage extended to the latter. The ongoing transformation of Iran's healthcare system, coupled with strategic initiatives like the consolidation under the Iran Health Insurance Fund and the embrace of digitalization, underscores a clear path towards greater efficiency, equity, and accessibility. Despite challenges related to stewardship and financing, the continuous efforts to control expenditures, extend free coverage to those in need, and enhance managerial expertise point to a resilient and forward-looking approach. Understanding these intricacies is vital for anyone navigating the Iranian healthcare landscape, ensuring peace of mind and access to quality medical care. We hope this comprehensive guide has illuminated the complexities and strengths of health insurance in Iran. If you have personal experiences or further insights to share, we encourage you to leave a comment below. Your perspectives contribute to a richer understanding for our community. For more detailed information on specific aspects of Iranian healthcare or insurance, explore our other related articles on this site.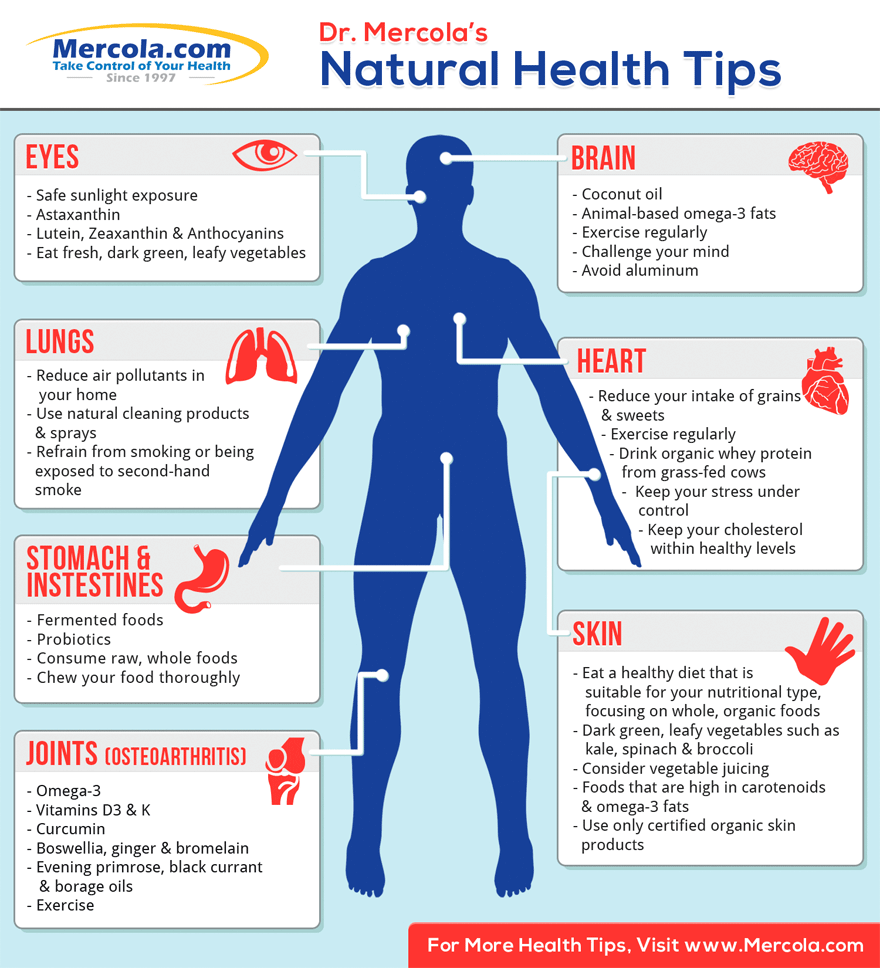
10 Health and Fitness Infographics That You Need To See
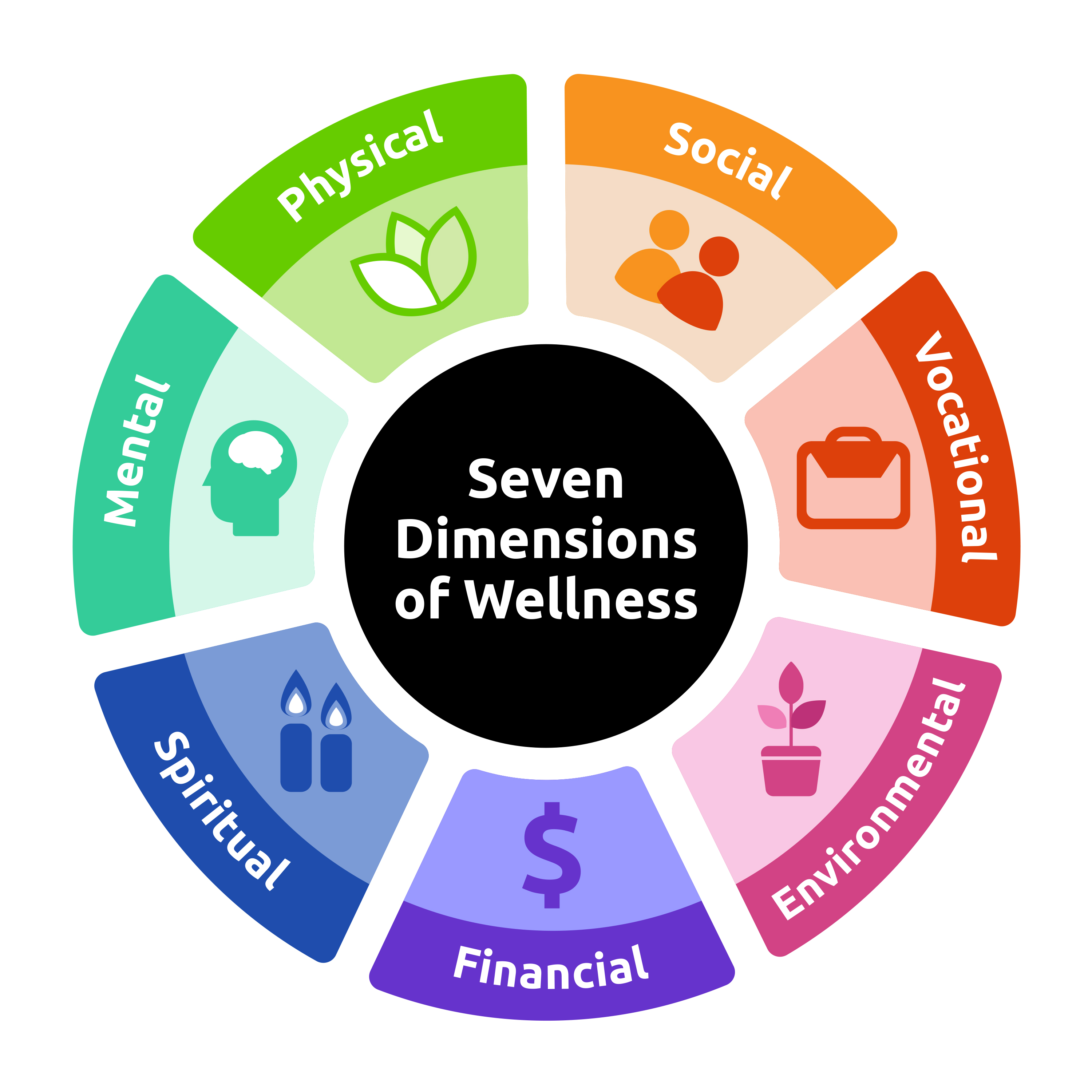
Health And Wellness 2023 - Image to u

All About Health | Rockford Regional Health Council